1/67
a well-combined, uniform mixture.
2/67
The inert gases of group 18 of the periodic table of the elements.
3/67
Two or more atoms held together in a covalent bond.
4/67
The number equal to the number of protons in an elements atom, that determines that element's chemical properties.
5/67
A natural protein that has catalytic properties.
6/67
A homogeneous mixture, formed from the dissolving of substances into one another. (Can be solid, liquid, or gas).
7/67
Any substance to the right of the "staircase" on the periodic table of the elements.
8/67
A compound containing only two elements.
9/67
Any one orbital of an atom around which electrons are found.
10/67
Any substance with a pH reading higher than 7, with the ability to neutralize an acid
11/67
The horizontal rows of the periodic table of the elements that indicates the amount of energy levels in an elements atom.
12/67
A change in a substance resulting in the alteration of one or more of its physical characteristics.
13/67
A substance made from only one type of atom.
14/67
(in grade 9 chemistry) the ability to conduct electricity.
15/67
The breaking down of a substance, in reaction to its surroundings.
16/67
The substance created by means of a chemical reaction.
17/67
A regular 3D geometric arrangement of particles.
18/67
A change in a substance resulting in the creation of an entirely new product.
19/67
neutrally charged part of an atom, that carries an atomic mass of 1.
20/67
The positively charged centre of the atom.
21/67
The scale that indicates whether a substance is basic or acidic, and to what degree.
22/67
A reaction that gives off energy in the form of heat.
23/67
The chemical change as a result of passing an electrical current through a substance.
24/67
The characteristic of a substance to be positively or negatively charged.
25/67
A chemical compound of hydrogen and oxygen atoms, that can create a basic substance.
26/67
A substance that cannot conduct electricity in any state of matter.
27/67
a compound of carbon and hydrogen atoms that is often found in products such as gasoline and propane.
28/67
Any substance with a pH reading lower than 7, with the ability to neutralize a base.
29/67
A substance that conducts electricity when in a solution or in an aqueous state.
30/67
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction, without being consumed in the process.
31/67
The production of water and salt, from the combination of an acid and a base.
32/67
Any substance that stops or slows a chemical reaction.
33/67
The substance that reacts in a chemical reaction to create the product.
34/67
Branch of natural science. (deals with the composition of substances).
35/67
The soft, light, reactive metals, found in group 1 of the periodic table of the elements.
36/67
A reaction that absorbs heat from its surroundings.
37/67
The law stating that the total mass of the reactant will equal the total mass of the product.
38/67
The negative ion of hydrogen, (which can have a positive or a negative charge).
39/67
The law stating that the amount of energy in a chemical equation stays the same from reactant to product.
40/67
positively charged part of an atom
41/67
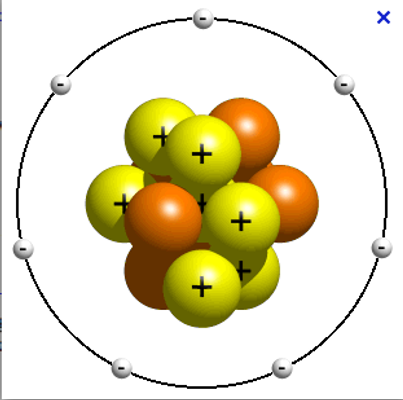
A type of drawing that depicts the atom as a small positively charged nucleus, surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
42/67
Vertical column in the periodic table of the elements, that contains elements with similar properties.
43/67
The number that indicates the amount of a chemical or chemical compound in a chemical equation.
44/67
A molecule, consisting of two atoms.
45/67
The simplest chemical substance that cannot be further broken down by chemical means.
46/67
The time it takes for any given reaction to take place.
47/67
Any substance near, or around the "staircase" on the periodic table of the elements. (They have the characteristics of both a metal and a non-metal).
48/67
Tabular chart of chemical elements according to their atomic number.
49/67
A compound that does not conduct electricity, composed of two non-metals.
50/67
A series of symbols that tell you if a substance is hazardous, and how.
51/67
The weighted average of the masses of all isotopes of an atom.
52/67
Combined elements in a fixed chemical bond.
53/67
Any element found in group 17 of the periodic table of the elements, that combine with a metal to form a salt
54/67
Smallest units of matter, that act as the building blocks of our world.
55/67
Has the ability to burn or corrode organic tissue/material.
56/67
The substances shown on the left side of the "staircase" on the periodic table of the elements.
57/67
A separated non-uniform mixture.
58/67
A substance that changes colour in reaction to coming in contact with either an acid or a base.
59/67
The group that establishes the official names for all chemical elements and compounds.
60/67
A compound that conducts electricity, made from a metal and a non-metal.
61/67
The theory stating that atoms are indestructible and indivisible, the mass of all atoms of a single element have the same mass, compounds are formed by two or more atoms, and that chemical reactions are a rearrangement of the atoms in a substance.
62/67
Any element found in group 2 of the periodic table of the elements.
63/67
Negatively charged part of an atom
64/67
The coating of a substance with a thin layer of metal by means of electroplating, to prevent corrosion.
65/67
The release of CO2 and H2O, due to a chemical compound being exposed to pure oxygen.
66/67
Sheets of paper that identify the hazards and safety measures, that need to be taken when handling a certain substance in the lab/work environment.