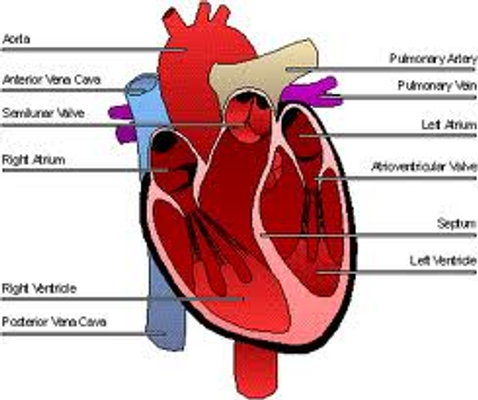
1/85
What is responsible for the storage of extra bile?
2/85
Platelets initiate ___
3/85
Water is absorbed primarily by the ___
4/85
The exchange of gases between the lungs and the blood occurs by the process of ___
5/85
The blood vessel that provides oxygen to the heart tissue is the ___
6/85
The microscopic anatomical unit of excretion found in the kidney is the ___
7/85
What is the change in the difference in positive and negative ions on the outer and inner surfaces of the neurons?
8/85
What is one word describing homeostasis?
9/85
What is the function of the epithelial?
10/85
Expired air will contain ____ than inspired air.
11/85
The sodium/potassium pump is primarily responsible for the ___
12/85
The primary function of the spiinal cord involve ____ between brain and spinal nerve.
13/85
The vocal cords are found in the ___
14/85
Which respiratory organ normally allows both air and food passage?
15/85
Which part of the brain contains centers for the heartbeat and respiration?
16/85
The part of the circulation involved with pumping blood to and from the lungs is the ___
17/85
What is the function of sodium bicarbonate in the digestive tract?
18/85
The urethra serves what other body system in males?
19/85
The digestive juices found in the stomach include
20/85
Which part of the brain is used to integrate incoming information and send it to the appropriate portion of the cerebrum?
21/85
The ___ functions to store food, kill bacteria, and partially digest proteins.
22/85
Contraction of the right ventricle forces blood initially into the ___
23/85
The air that is moved in and out with each normal breath is termed the ___
24/85
Which blood vessels carry blood away from the heart?
25/85
The rate of breathing is chiefly dependent on chemical factors in the blood, of which the most important is ___
26/85
If a person has a blood pressure of 120/80, the "120" refers to the ____
27/85
What is the function of connective tissue?
28/85
Spnal nerves contain ___
29/85
What is the function of the nervous tissues?
30/85
Which are cell fragments that help initiate blood clotting?
31/85
In the processing of food through the digestive tract, what is the correct order?
32/85
Muscles are connected to bones by ___
33/85
Which is not a major function of the respiratory tract?
34/85
Microvilli forma brush border on the cells of the ___
35/85
The urinary bladder is useful because it ___
36/85
Food is prevented from entering the trachea by ____
37/85
The membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord are called ___
38/85
Which type of muscle is involuntary and lacks striations?
39/85
Name the accessory glands in the digestive system.
40/85
An increased amount of ADH leads to
41/85
Excretion is a process in which ___ is removed from the body.
42/85
Red blood cells are red due to ____
43/85
Most of the carbon dioxide transported in the plasma is in the form of ___
44/85
What are the basic types of tissue?
Hint: 4 choices
45/85
In the body, glucose is stored in the liver as ____
46/85
The type of respiration in which ATP is produced is called ___
47/85
A reflex action is ___
48/85
The pH of the stomach is usually about _
49/85
Which of the following in NOT a function of the digestive system?
50/85
Which blood vessels will have walls only one cell thick?
51/85
Which portion of the respiratory tract is commonly referred to as the "throat"?
52/85
In the axon, the nerve impulses travel ___
53/85
Which molecule is responsible for the waterproofing of the skin?
54/85
In the body, glucose is stored in the liver as ____
55/85
Trace the path of an inhaled air molecule.
56/85
What is the function of muscle tissue?
57/85
The tube that transports urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder is the ___
58/85
A nerve is composed of ____
59/85
In humans, digestion of starches begins in the ____
60/85
The Adam's apple is actually a part of the ___
61/85
Melanin is a substance responsible for ____
62/85
Which type of cell is used to carry oxygen in the blood?
63/85
The blood that enters the coronary artery comes from the ___
64/85
Nitrogenous wastes are produced by the ___
65/85
The part of the skin that has adipose tissue to help insulate the body is the ___
66/85
Neurtransmitters are molecules that cross the synaptic cleft and either excite or inihibit the ____
67/85
Name the tissue in which the cells are separated by a liquid.
68/85
The main function of the cerebrospinal fluid is protection of ___
69/85
The pacemaker of the heart is termed the
70/85
What does HCl activate in the stomach?
71/85
Which layer of the skin protects the body from bacterial infection and water loss?
72/85
The physical principle upon which kidney dialysis is based is ___
73/85
The glomerular capsule ____
74/85
Which lobe of the cerebrum is responsible for vision?
75/85
Which part of the respiratory system is composed of C-shaped cartilaginous rings and cilia?
76/85
Sysotle occurs when the heart is ___
77/85
Dendrites carry impulses ___
78/85
Higher than normal blood pressure is called ___
79/85
The ____ capillaries are enclosed by the glomerular (Bowman's) capsule.
80/85
The alveoli are kept open by ____ so that gas exchange can take place.
81/85
The entrace and exit of air into and out of the lungs is called ___
82/85
Reabsorption occurs in the ____ of the nephron
83/85
Heartburn occurs when ____
84/85
Villi serve to ___